Frontiers Multiple Ehrlichia chaffeensis genes critical for persistent infection in a vertebrate host are identified as nonessential for its growth in the tick vector; Amblyomma americanum
Di uno scrittore di uomini misteriosi
Descrizione
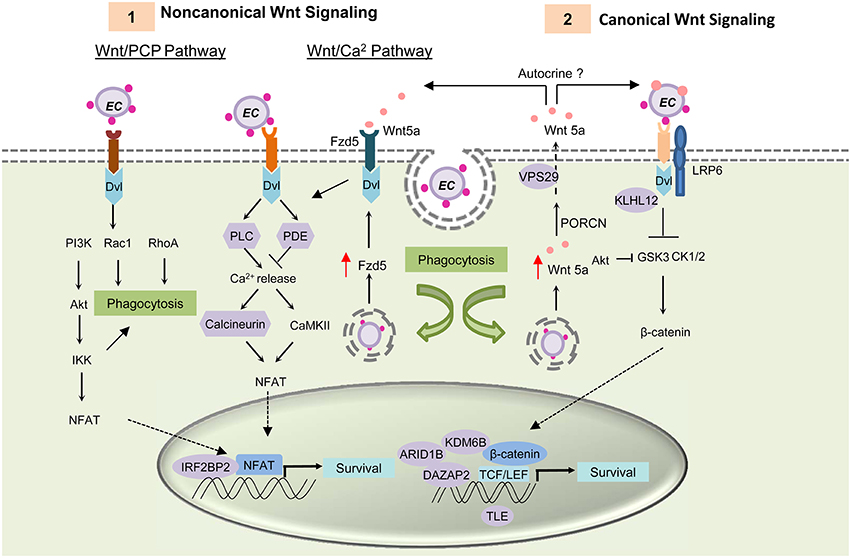
Frontiers Hacker within! Ehrlichia chaffeensis Effector Driven Phagocyte Reprogramming Strategy

An Entry-Triggering Protein of Ehrlichia Is a New Vaccine Candidate against Tick-Borne Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis
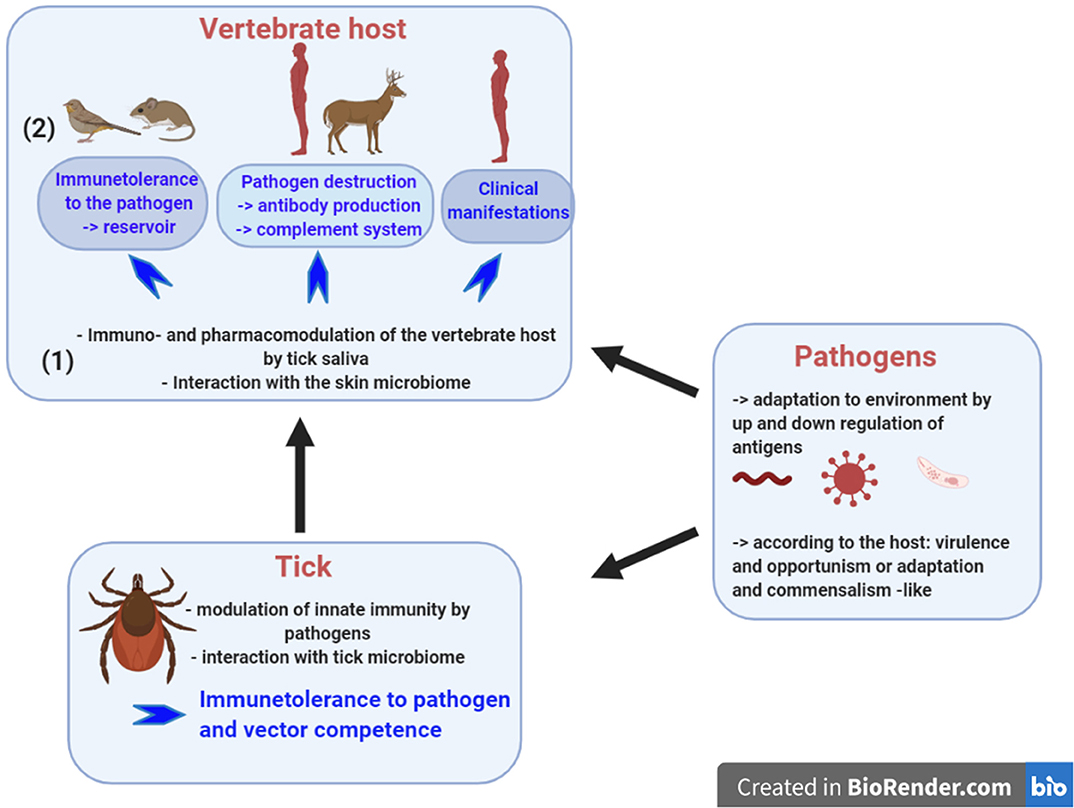
Frontiers Induced Transient Immune Tolerance in Ticks and Vertebrate Host: A Keystone of Tick-Borne Diseases?
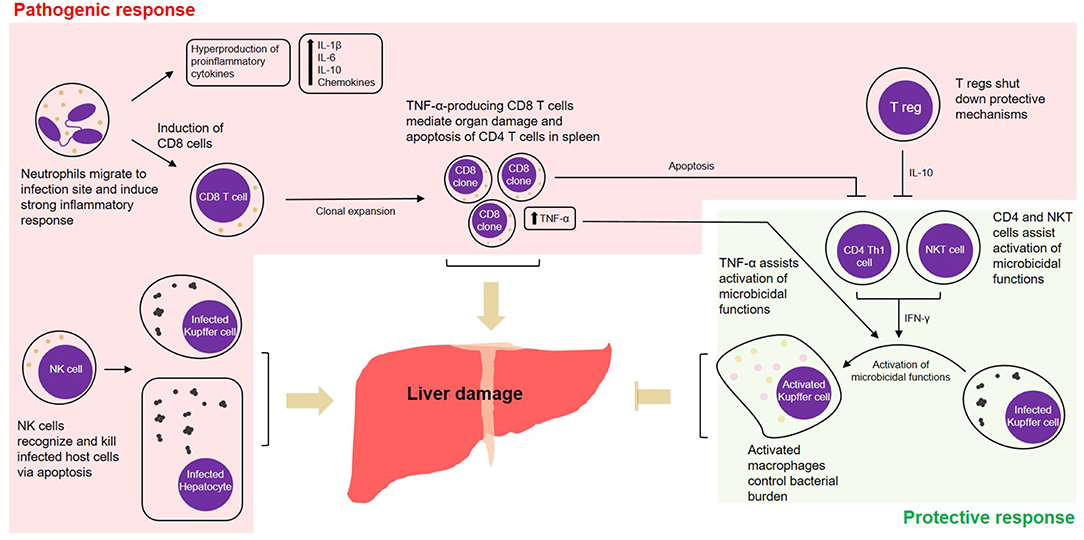
Frontiers Emerging Roles of Autophagy and Inflammasome in Ehrlichiosis

Emerging horizons for tick-borne pathogens: from the 'one pathogen–one disease' vision to the pathobiome paradigm
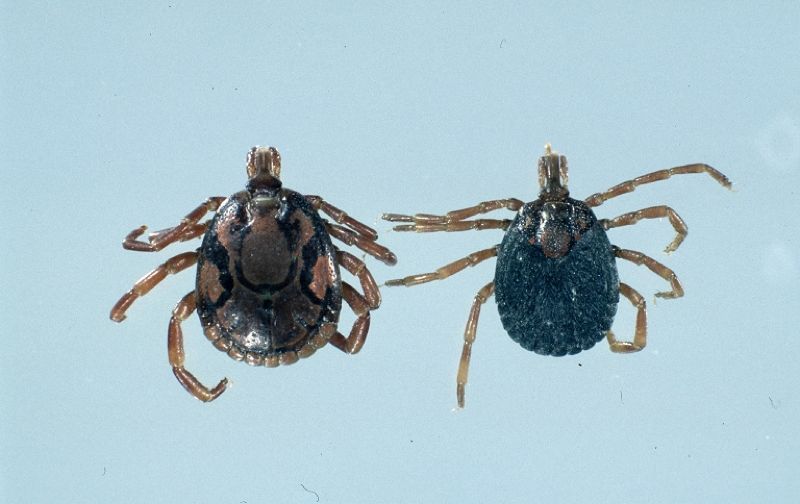

ENY-2067/IN1327: Ehrlichia and Anaplasma

Multi-Locus Sequence Typing of Ehrlichia chaffeensis Reveals Extensive Genotypic Variation across the United States in: The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Volume 104 Issue 4 (2021)

Ehrlichia develops highly adaptative strategies inside host cell. (1)
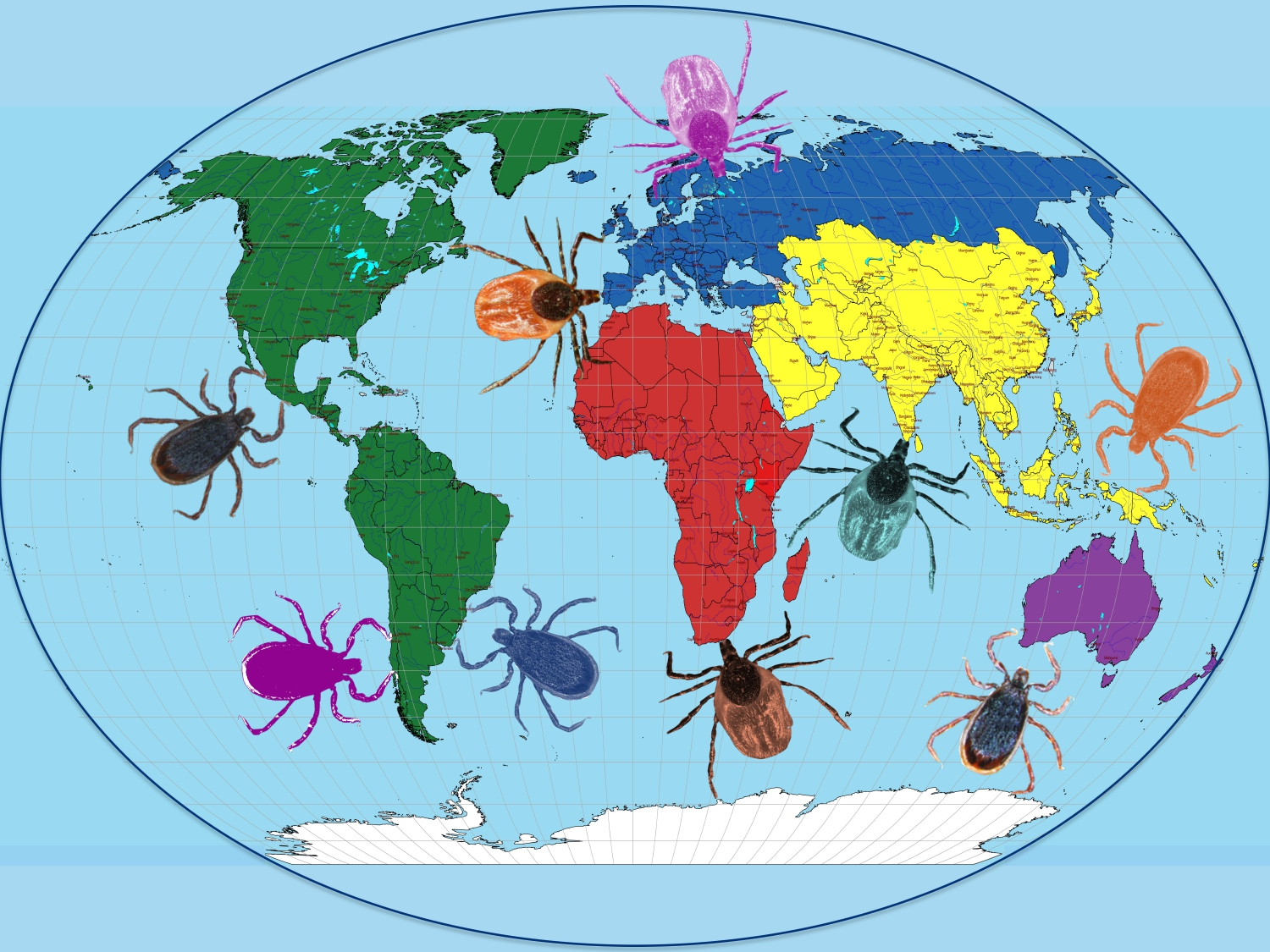
Pathogens, Free Full-Text
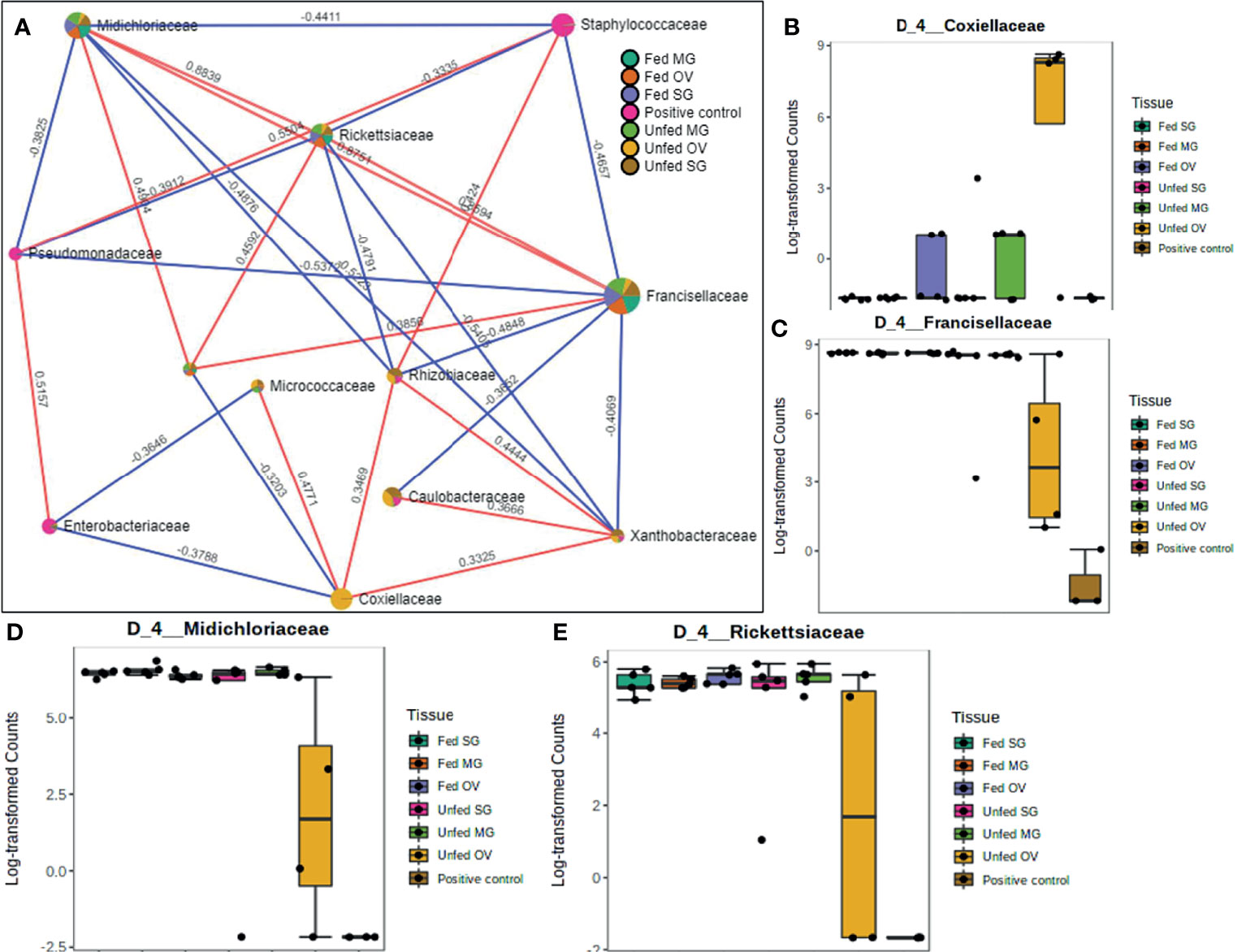
Frontiers Recently Evolved Francisella-Like Endosymbiont Outcompetes an Ancient and Evolutionarily Associated Coxiella-Like Endosymbiont in the Lone Star Tick (Amblyomma americanum) Linked to the Alpha-Gal Syndrome

Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
Frontiers Multiple Ehrlichia chaffeensis genes critical for persistent infection in a vertebrate host are identified as nonessential for its growth in the tick vector; Amblyomma americanum
da
per adulto (il prezzo varia in base alle dimensioni del gruppo)







