Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics
Di uno scrittore di uomini misteriosi
Descrizione

Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws after tooth extraction in senescent female mice treated with zoledronic acid: microtomographic, histological and immunohistochemical characterization

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Pathophysiology of Medication‐Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—A Minireview - Tetradis - 2023 - JBMR Plus - Wiley Online Library

Infection and Medication-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw - H. Katsarelis, N.P. Shah, D.K. Dhariwal, M. Pazianas, 2015

Cells, Free Full-Text
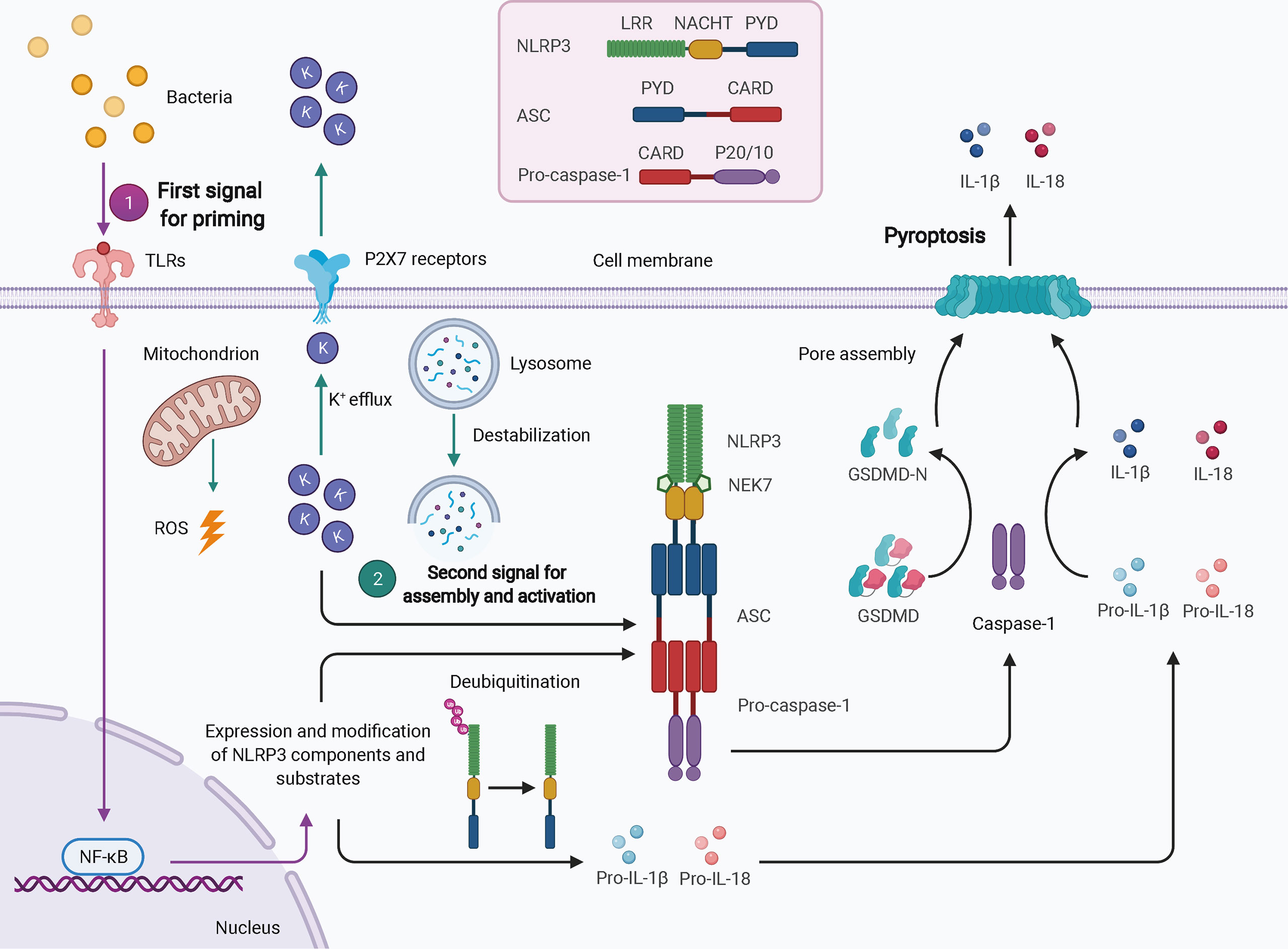
Frontiers Inflammasomes in Alveolar Bone Loss
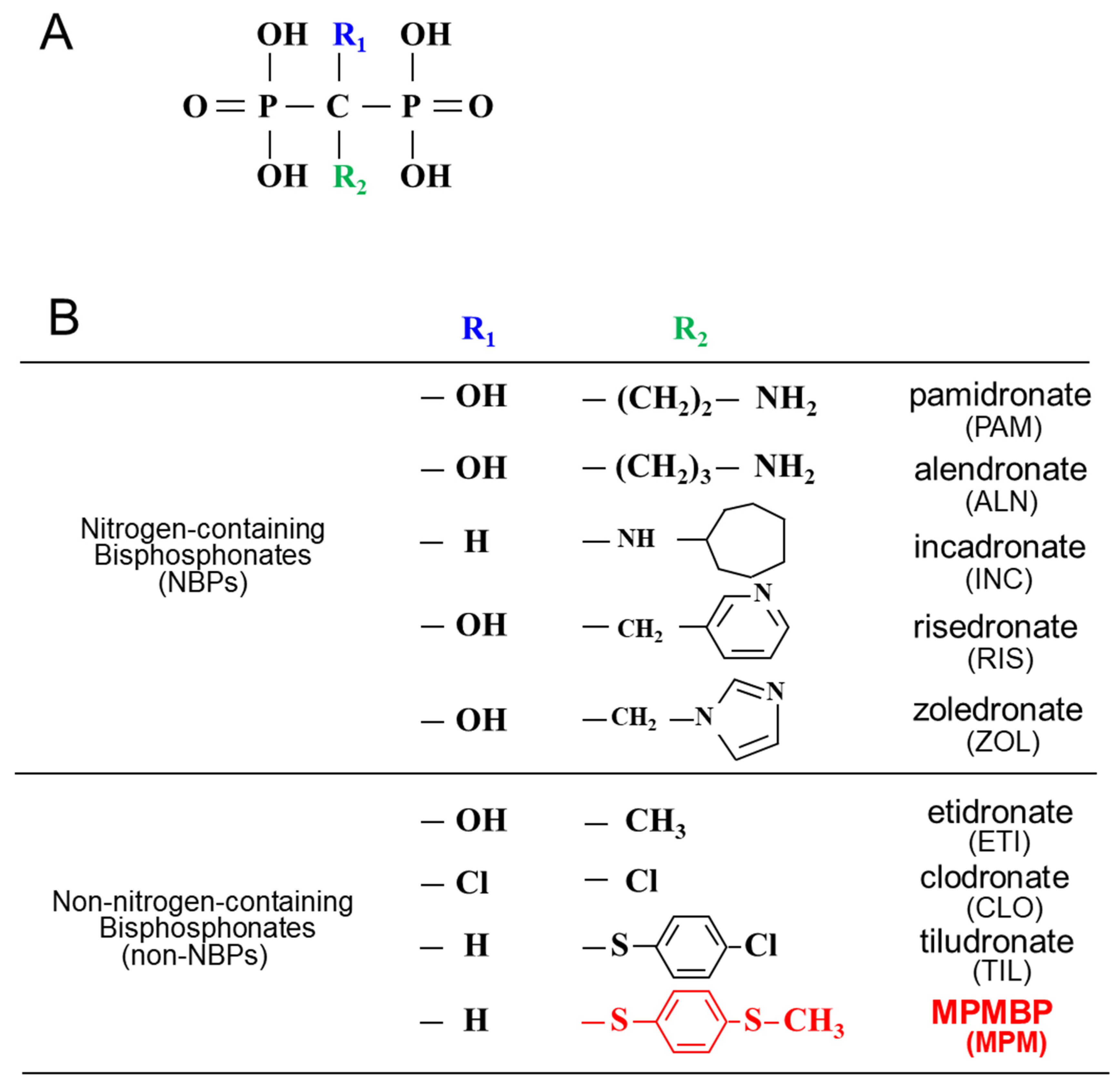
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
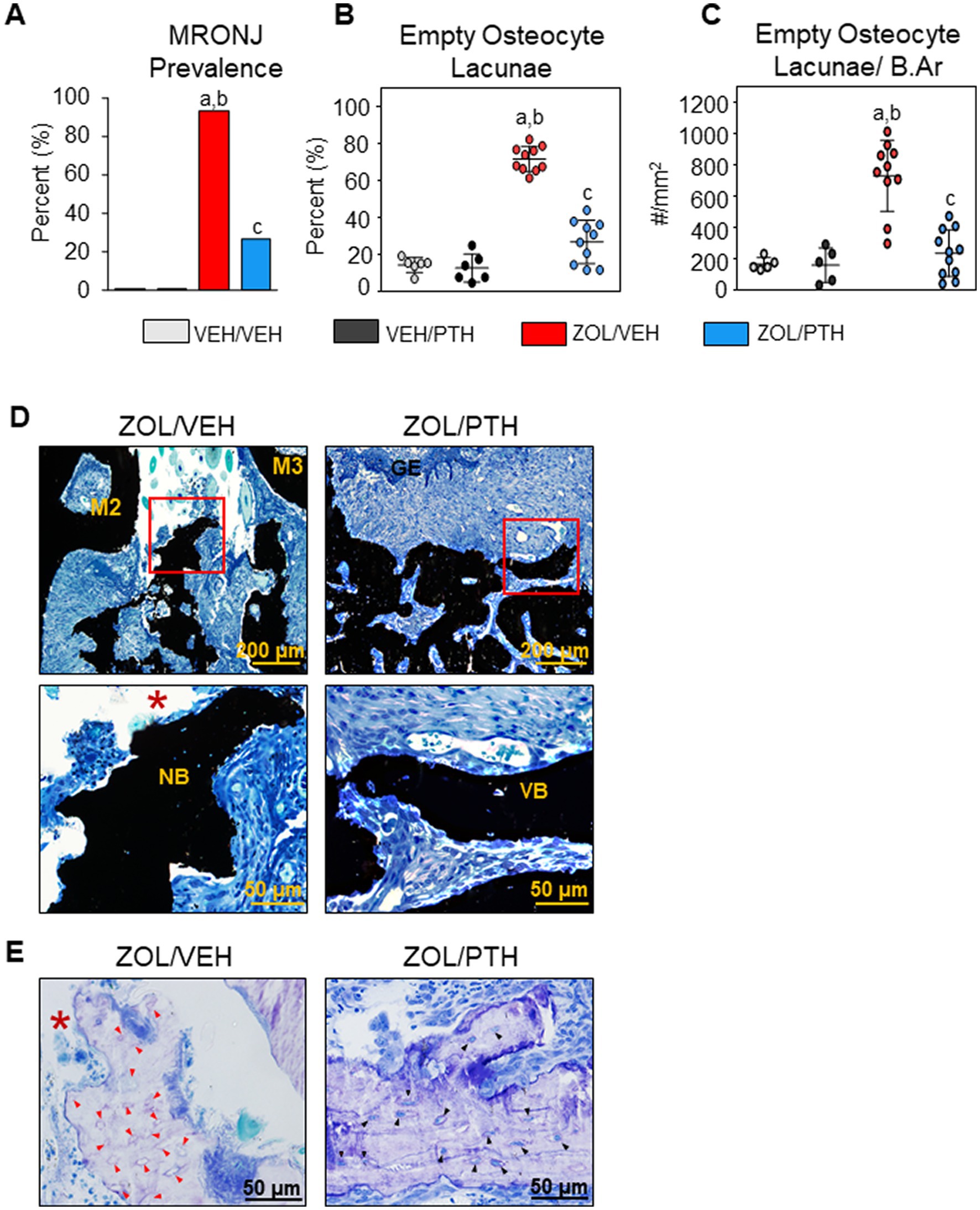
Frontiers Intermittent parathyroid hormone enhances the healing of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw lesions in rice rats

Tooth extraction in mice administered zoledronate increases inflammatory cytokine levels and promotes osteonecrosis of the jaw

Mechanism of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) revealed by targeted removal of legacy bisphosphonate from jawbone using equilibrium competing inert hydroxymethylene diphosphonate
da
per adulto (il prezzo varia in base alle dimensioni del gruppo)







